Math 276
Calculus III
Fall 2005
Dr. Constant J. Goutziers
Department of Mathematics, Computer Science and Statistics
goutzicj@oneonta.edu
Lesson 10
Functions of Several Variables
Initializations
| > |
restart;
with(plots):
setoptions3d(axes=boxed);
|
Warning, the name changecoords has been redefined
10.1 Definition and Plotting of Functions of two Variables
Examples
Example 10.1.1
Define
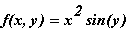 as a Maple function and sketch its graph.
as a Maple function and sketch its graph.
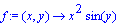
| > |
plot3d(f(x, y), x=-2..2, y=-10..10, style=patch, labels=[x,y,z], grid=[20,80]);
|
![[Maple Plot]](images/Lesson_103.gif)
Example 10.1.2
Sometimes graphing routines have difficulties with surfaces that have vertical tangent planes. For instance try to plot the graph of
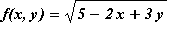 .
.
| > |
f:=(x,y)->sqrt(5-2*x+3*y);
|
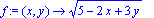
| > |
plot3d(f(x,y), x=-3..3, y=-3..3, orientation=[-20,60], labels=[x,y,z]);
|
![[Maple Plot]](images/Lesson_106.gif)
A way to remedy this problem is to parametrize this surface in such a way that one of the parameters is constant along the line
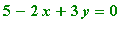 , where the vertical tangent plane occurs. For instance let
, where the vertical tangent plane occurs. For instance let
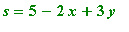 and use x and s as parameters.
and use x and s as parameters.
| > |
eq:=op(1, f(x,y))=s;
rr:=isolate(eq, y);
|
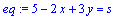
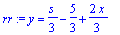
| > |
plot3d(subs(rr, [x,y,f(x,y)]), x=-3..3, s=0..10, orientation=[-20,60], labels=[x,y,z]);
|
![[Maple Plot]](images/Lesson_1011.gif)
Example 10.1.3
Define
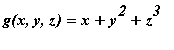 as a Maple function and evaluate
as a Maple function and evaluate
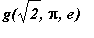 .
.
| > |
g:=(x, y, z)->x+y^2+z^3;
|
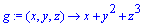
| > |
g(sqrt(2), Pi, exp(1));
|
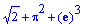
10.2 Contour Plots and Level Curves
In stead of a surface plot, like the one produced in Example 10.1.1 for the function
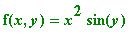 , we can produce a set of level curves. A level curve is the projection on the XOY-plane aof a path on the surface z=f(x, y) with constant z-coordinate. The Maple syntax for producing level curves is
contourplot
or
contourplot3d
. Both routines are located in the
plots
package.
, we can produce a set of level curves. A level curve is the projection on the XOY-plane aof a path on the surface z=f(x, y) with constant z-coordinate. The Maple syntax for producing level curves is
contourplot
or
contourplot3d
. Both routines are located in the
plots
package.
Examples
Example
Create a contourplot for the function
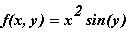 , first by using
contourplot
, then by using
contourplot3d
.
, first by using
contourplot
, then by using
contourplot3d
.
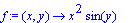
| > |
contourplot(f(x, y), x=-2..2, y=-10..10, numpoints=3600);
|
![[Maple Plot]](images/Lesson_1019.gif)
The advantages of using contourplot3d instead of contourplot are that the contourplot3d is faster and allows for more detailed color control. the color control allows the user to identify high levels (red) and low levels (purple).
| > |
contourplot3d(f(x, y), x=-2..2, y=-10..10, shading=ZHUE, axes=boxed, orientation=[-90, 0], numpoints=2500);
|
![[Maple Plot]](images/Lesson_1020.gif)
A similar picture can be obtained by using the
plot3d
command with a
style=patchcontour
option.
| > |
plot3d(f(x, y), x=-2..2, y=-10..10, shading=ZHUE, style=patchcontour, axes=boxed, orientation=[-90, 0], numpoints=2500);
|
![[Maple Plot]](images/Lesson_1021.gif)
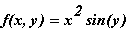 as a Maple function and sketch its graph.
as a Maple function and sketch its graph.
![]()
![[Maple Plot]](images/Lesson_103.gif)
![]() .
.
![]()
![[Maple Plot]](images/Lesson_106.gif)
![]() , where the vertical tangent plane occurs. For instance let
, where the vertical tangent plane occurs. For instance let
![]() and use x and s as parameters.
and use x and s as parameters.
![]()
![]()
![[Maple Plot]](images/Lesson_1011.gif)
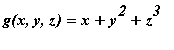 as a Maple function and evaluate
as a Maple function and evaluate
![]() .
.
![]()
![]()
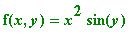 , we can produce a set of level curves. A level curve is the projection on the XOY-plane aof a path on the surface z=f(x, y) with constant z-coordinate. The Maple syntax for producing level curves is
contourplot
or
contourplot3d
. Both routines are located in the
plots
package.
, we can produce a set of level curves. A level curve is the projection on the XOY-plane aof a path on the surface z=f(x, y) with constant z-coordinate. The Maple syntax for producing level curves is
contourplot
or
contourplot3d
. Both routines are located in the
plots
package.
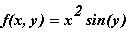 , first by using
contourplot
, then by using
contourplot3d
.
, first by using
contourplot
, then by using
contourplot3d
.
![[Maple Plot]](images/Lesson_1019.gif)
![[Maple Plot]](images/Lesson_1020.gif)
![[Maple Plot]](images/Lesson_1021.gif)