Works clearly related to the style found in the Hours of Jeanne d'Évreux can be found through much of the fourteenth century. Until it was discovered that Pucelle died in 1334, these works were attributed to Pucelle himself based on their similarity to the work in the Hours of Jeanne d'Évreux. Now it is seen that the later works are probably by an artist trained in Pucelle's workshop who took over the shop after the master's death. Among the books associated with this later history of the Pucelle style are the following examples:
Hours of Jeanne de Navarre, probably after 1336:
Psalter of Bonne de Luxembourg, between 1332-1349:

Hours of Yolande of Flanders, after 1350 (manuscript badly damaged in the nineteenth century):


Breviary of Charles V, between 1358 and 1380:

Petites Heures of John of Berry, first stage produced probably between 1372-75; the rest of the manuscript around 1380's.


This follower of Jean Pucelle has been identified as Jean Le Noir. Jean Le Noir is first recorded in 1332 and again in 1337 as living on the Rue Erembourg de Brie, the same street Jean Pucelle lived on. He is listed as Jehan Lenoir, enluminieur. Documents show that Jean Le Noir was successively in the service of Yolande of Flanders, Charles V, and Jean de Berry. A document of 1358, states that Jean Le Noir left the service of Yolande de Flandre and along with his daughter Bourgot, who is identified as enlumineresse, entered the service of King John the Good and his son the dauphin Charles. This document also records the gift of a house to Jean in Paris on the Rue Trousevache. In 1372 there are records in the accounts of Jean de Berry of gifts of cloth to Le Noir. In 1375, Le Noir is again listed as receiving payments from Berry. In this document he is listed as "enlumineur du roy et de mon dit seigneur."* By 1375, Le Noir had moved from Paris to Bourges. The correspondences between this documentary record of Jean Le Noir and the patronage of these manuscripts in the Pucelle style create a compelling argument to identify Jean Le Noir as this inheritor of the Pucelle workshop.
Comparison of corresponding scenes from these manuscripts reveals the continuity of designs as well as significant modifications. For example compare these images of the Betrayal from these four manuscripts:

|

|

|

|
Compare the following representations of the Crucifixion:

|

|

|

|
Compare the following representations of the Entombment:

|

|

|
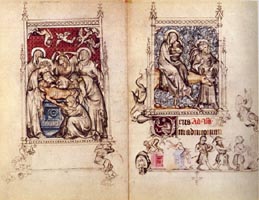
|
A comparison of the Annunciation of the Shepherds in the Hours of Jeanne d'Évreux to the same subject in the Hours of Jeanne de Navarre shows a good example of the reuse of models:

|

|
The latest work attributed to Jean Le Noir appears to be the Passion scenes apparently painted in the Petites Heures between 1372-75. These images are worthwhile to look at in detail as a narrative of the story of the passion. What responses do you have to these scenes? Write them in your journal.
|
Petites Heures |
Hours of Jeanne d'Evreux |

|
|

|
|

|
|