PHYS103 Fall 2005 Homework 3
Giancoli Sixth Edition Chapter 2
Questions 13
Problems 23, 25, 27,
35, 36, 39, 47
Answers to Questions
13. As a freely falling object speeds up, its acceleration due to
gravity stays the same. If air resistance
is considered, then the acceleration of the object is due to both gravity and
air resistance. The total acceleration
gets smaller as the object speeds up, until the object reaches a terminal
velocity, at which time its total acceleration is zero. Thereafter its speed remains constant.
Solutions to Problems
23. Assume that the plane starts from rest. The runway distance is found by solving Eq. 2-11c for ![]() .
.

25. The words “slowing down uniformly” implies
that the car has a constant acceleration.
The distance of travel is found form combining Eqs.
2-7 and 2-8.
![]() .
.
6. The final velocity of the car is zero. The initial velocity is found from Eq. 2-11c with ![]() and solving for
and solving for ![]() .
.
![]()
27. The final velocity of the driver is zero. The acceleration is found from Eq. 2-11c with ![]() and
and
solving
for ![]() .
.
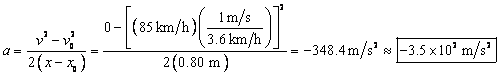
Converting to "g's": 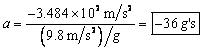 .
.
35. Choose downward to be the positive direction, and take ![]() to be at the top of
the
to be at the top of
the ![]() , and the acceleration is
, and the acceleration is ![]() .
.
(a) The elapsed time can be found from Eq. 2-11b, with x
replaced by y.
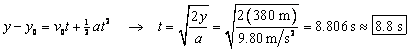 .
.
(b) The final velocity can be found from equation
(2-11a).
![]()
36. Choose upward to be the positive direction, and take ![]() to be at the height
where the ball was hit. For the upward
path,
to be at the height
where the ball was hit. For the upward
path, ![]() ,
, ![]() at the top of the
path, and
at the top of the
path, and ![]() .
.
(a) The displacement can be found from Eq. 2-11c, with x
replaced by y .
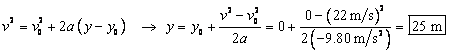
(b) The time of flight can be found from
Eq. 2-11b, with x
replaced by y ,
using a displacement of 0
for the displacement of the ball
returning to the height from which it was hit.
![]() The result of t = 0
s is the time for the original displacement of zero (when the ball was hit),
and the result of t = 4.5 s is the
time to return to the original displacement.
Thus the answer is t = 4.5
seconds.
The result of t = 0
s is the time for the original displacement of zero (when the ball was hit),
and the result of t = 4.5 s is the
time to return to the original displacement.
Thus the answer is t = 4.5
seconds.
39. Choose downward to be the positive direction, and take ![]() to be the height where
the object was released. The initial velocity is
to be the height where
the object was released. The initial velocity is ![]() , the acceleration is
, the acceleration is ![]() , and the displacement of the package will be
, and the displacement of the package will be ![]() . The time to reach
the ground can be found from Eq. 2-11b, with x replaced by y.
. The time to reach
the ground can be found from Eq. 2-11b, with x replaced by y.
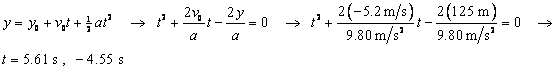
The correct time is the positive
answer, ![]() .
.
47. Choose downward to be the positive direction, and ![]() to be at the top of
the cliff. The initial velocity is
to be at the top of
the cliff. The initial velocity is ![]() , the acceleration is
, the acceleration is ![]() , and the final location is
, and the final location is ![]() .
.
(a) Using Eq.
2-11b and substituting y for x, we have
![]() . The positive answer
is the physical answer:
. The positive answer
is the physical answer: ![]() .
.
(b) Using Eq.
2-11a, we have ![]() .
.
(c) The total distance traveled
will be the distance up plus the distance down.
The distance down will be 70 m more than the distance up. To find the distance up, use the fact that
the speed at the top of the path will be 0.
Then using Eq. 2-11c:
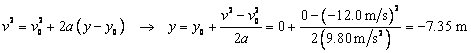 .
.
Thus the distance up is 7.35 m, the distance down is
77.35 m, and the total distance traveled is ![]() .
.